2025/12/17
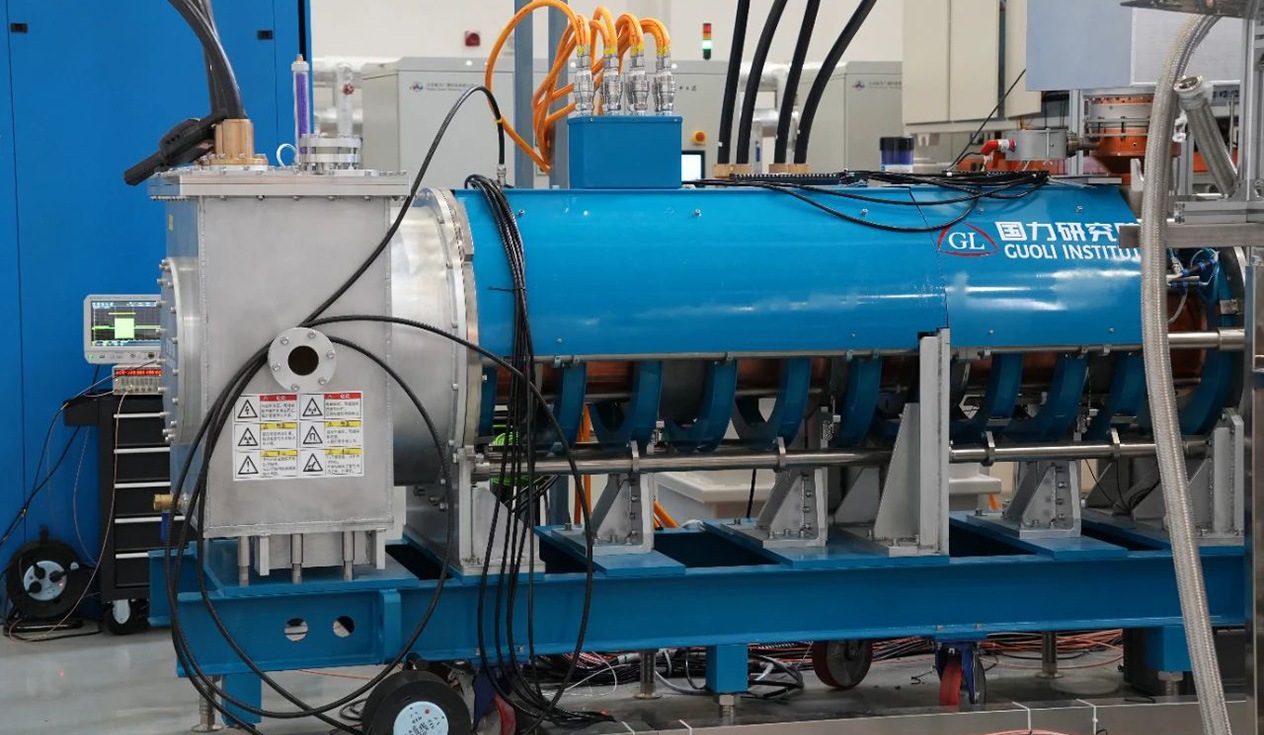
As a core device capable of efficiently generating microwave energy, the magnetron has continuously shattered boundaries in energy applications since its inception. By leveraging the synergistic interaction between magnetic and electric fields, magnetrons produce microwaves that possess unique characteristics—deep penetration, thermal effects, and non-thermal effects. These properties enable magnetrons to play an irreplaceable role across diverse industrial sectors such as rubber devulcanization, semiconductor manufacturing, and metal smelting, as well as in everyday domains like food processing and sterilization. From heavy-duty industrial production lines to refined consumer services, high-power magnetrons are reshaping technological pathways across numerous industries.
I. Microwave-Driven Innovation in Industrial Manufacturing
01. Rubber Industry
In the rubber industry, traditional vulcanization processes require prolonged heating, resulting in high energy consumption and low efficiency. The application of magnetron technology has transformed this paradigm. Microwaves enable molecular-level, uniform heating of rubber materials, significantly shortening vulcanization time while reducing energy usage. This advancement not only boosts production efficiency but also enhances the physical properties of rubber products—improving wear resistance and elasticity. Consequently, the quality of tires, seals, and industrial belts has markedly improved, delivering tangible benefits to automotive manufacturing and mechanical engineering sectors.

02. Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry demands extreme precision, and magnetron technology offers solutions that meet these stringent requirements. In plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) processes, microwaves generated by magnetrons excite gases to produce plasmas, enabling the deposition of films that are exceptionally uniform and dense—critical for fabricating advanced semiconductor chips.

03. Synthetic Diamond Production
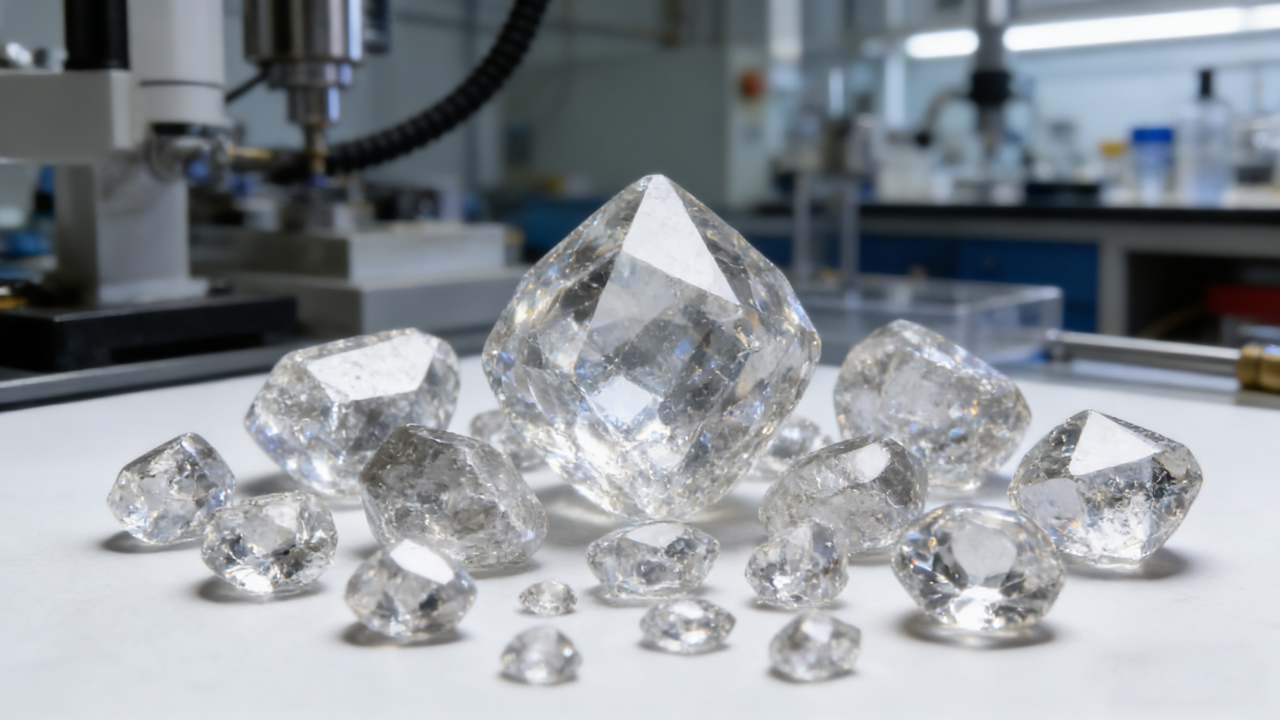
The synthesis of synthetic diamonds exemplifies the outstanding capabilities of magnetron technology. Under high-temperature, high-pressure conditions, microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (MPCVD) is currently regarded as the optimal method for growing single-crystal diamonds. These synthetic diamonds serve not only the jewelry industry but also play indispensable roles in high-end cutting tools, thermal management materials, and optical components.

II. Microwave Applications in Food and Healthcare
01. Food Industry
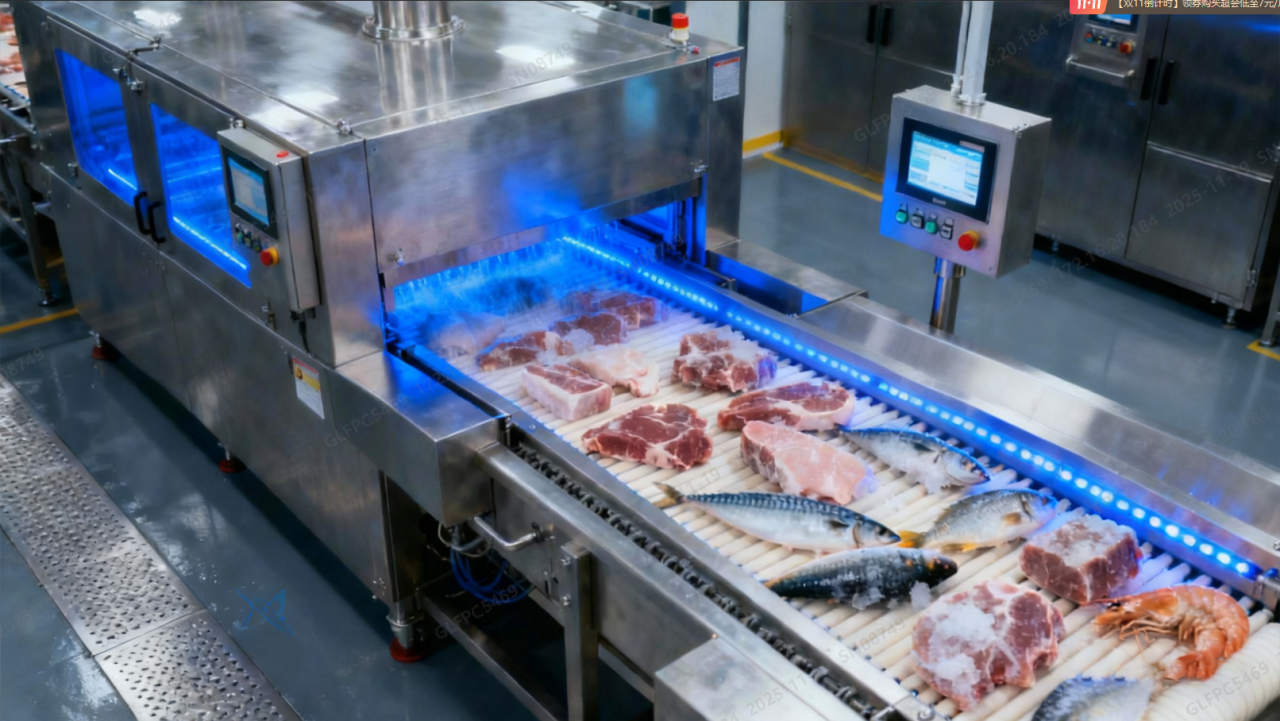
Microwave thawing technology addresses the quality degradation issues associated with conventional thawing methods. Microwaves generated by magnetrons penetrate food surfaces, allowing internal ice crystals to absorb energy simultaneously—enabling rapid and uniform defrosting. Compared to air or water thawing, microwave thawing reduces processing time by 70%–90%, significantly lowering the risk of microbial growth while preserving the original flavor and nutritional content of food. This technology is widely adopted in the processing of meat, seafood, and ready-to-eat meals.

02. Drying and Dehydration
Magnetron technology also excels in drying and dehydration applications. Unlike hot-air drying, microwave drying generates heat from within the material, dramatically accelerating moisture migration and shortening drying times. This method is especially suitable for heat-sensitive products such as vegetables, fruits, and traditional Chinese medicinal herbs, effectively preserving their active compounds and natural color.

03. Medical Field
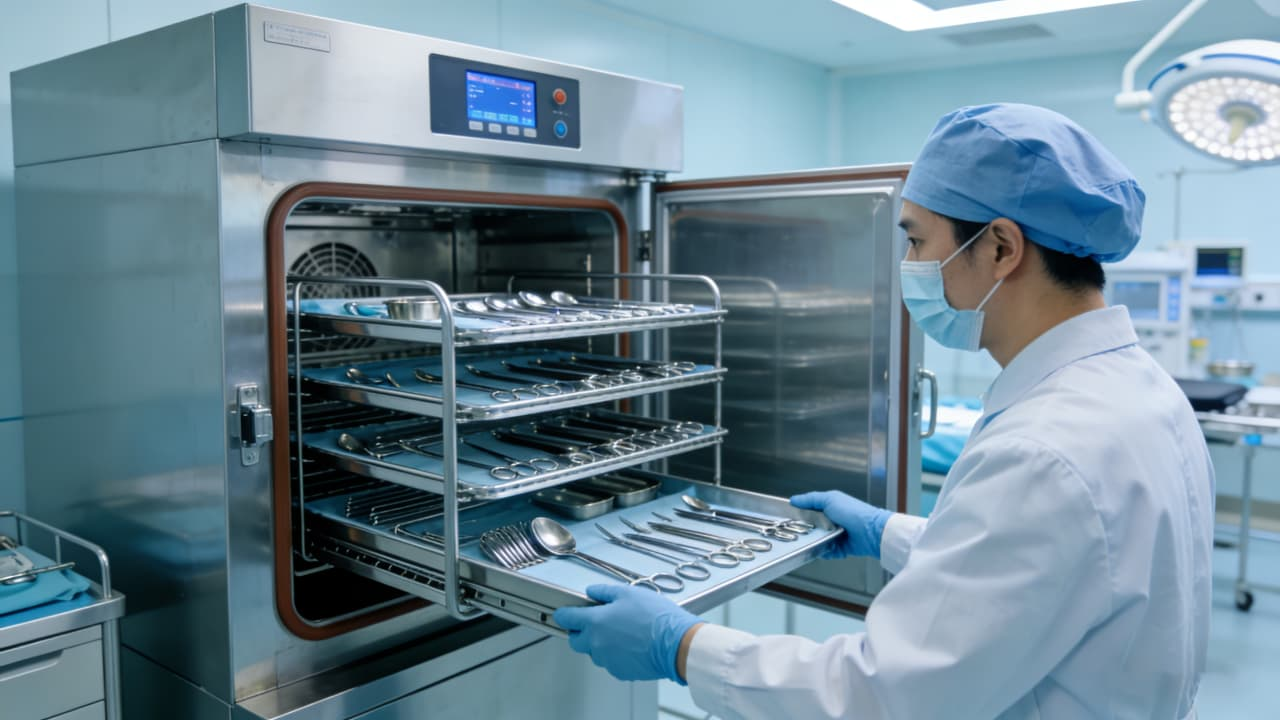
Microwave sterilization represents another critical application of magnetrons in healthcare and food safety, leveraging both thermal and non-thermal effects. The thermal effect refers to the rise in temperature caused by microwave absorption, which achieves sterilization; the non-thermal effect disrupts microbial nutrient cells or damages enzymatic systems within microorganisms, leading to their inactivation or death. Compared to chemical sterilization, microwave sterilization leaves no chemical residues and avoids secondary contamination. In contrast to conventional dry-heat sterilization, it operates in far less time and can penetrate packaging materials, enabling sterilization of sealed items.

With ongoing advances in materials science and electronics, magnetron technology is evolving toward higher efficiency, more precise control, and broader applicability. From facilitating chemical bonding in rubber vulcanization and crystal growth in diamond synthesis, to enabling nanoscale precision in semiconductor fabrication and everyday food thawing, magnetron technology has permeated virtually every facet of modern industry and daily life. As innovation continues, high-power magnetrons will undoubtedly unlock even greater value across emerging fields, driving industrial transformation and enhancing quality of life.
In this era where microwaves are ubiquitous, we are witnessing how a single form of energy is quietly revolutionizing the way we manufacture and live.
Latest News
Get Professional Solutions
We are looking forward to engaging with you to explore more solutions for electric vacuum devices.